More functions from the
<math.h> or <cmath> header files. Today it’s
about the fmod function.
The modulus operator, %, returns the remainder of a over b.
For example, 5
% 2 = 1 since 4, a multiple of 2, plus 1, the remainder, equals 5. The
modulus operator however can only be used with whole numbers. The fmod
function applies the same principle to floating-point numbers.
From C11 standard.
Test Code.
I tested the functions in Visual C++ 2010 as an console
application.
// The
standard library includes the system function.
#include <cstdlib>
// C++
standard I/O library.
#include <cstdio>
// C++ math
library.
#include <cmath>
int main()
{
// Header.
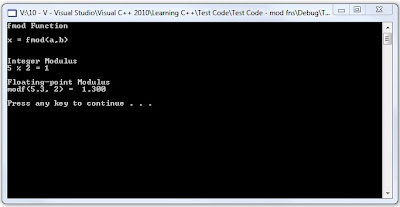
printf("fmod
Function\n\n");
printf("x
= fmod(a,b) \n\n\n");
printf("Integer
Modulus\n");
printf("5
%% 2 = %d", 5 % 2);
printf("\n\nFloating-point
Modulus\n");
printf("modf(5.3,
2) = %6.3f\t", fmod(5.3, 2.0));
printf("\n\n");
// Keep console
window open.
system("pause");
// Return some
value.
return 0;
} // end main
Output.


No comments:
Post a Comment